Chinese researchers are tackling dendrite formation in zinc-ion batteries with the development of an anisotropic and biodegradable separator inspired by wood.
The new separator, reported in Nature Communications, is called V-NFC-CS and is constructed from nano-fibrillated cellulose (NFC) and chitosan, made through an innovative directional freezing technique.
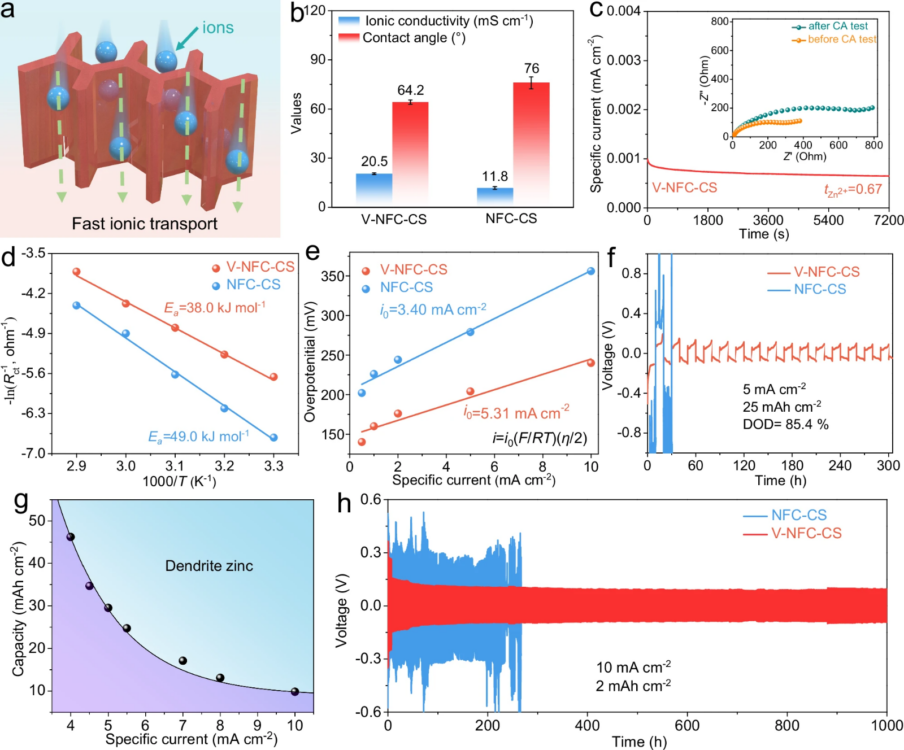
The paper claims the design significantly improves the modulus along the oriented direction while simultaneously facilitating fast zinc ion transport through aligned vertical channels.
The configuration also resolves the contradiction between low separator thickness and good dendrite-inhibition capability, it stated.
Thickness is reduced to 23 microns. The research team said the anisotropic separator realises a prolonged life span for Zn||Zn cells, along with improved cyclability in full batteries.
The challenges that persist notably pertain to zinc dendrite formation, corrosion and hydrogen evolution reaction at the zinc electrode surface, the researchers said.
Methods to address these include zinc electrode surface coatings, zinc electrode structure design, electrolyte additive modifications and hydrogel electrolyte utilisation.
The glass fibre separators widely used at present are expensive, have excessive thickness (typically >200 microns), and cannot effectively resist zinc dendrites, according to the paper.
“Consequently, there is a pressing need to optimize AZIB separators. Despite various strategies proposed to address these issues, the reduction of separator thickness and the improvement of dendrite suppression effect often cannot be achieved simultaneously,” they said.
A thinner separator is beneficial to the improvement in battery energy density. The aim is to reduce thickness further, they said.
The researchers are Hong Ma, Hongli Chen, Minfeng Chen, Anxin lithium, Xiang Han, Dingtao Ma, Peixin Zhang and Jizhang Chen; from Co-Innovation Center of Efficient Processing and Utilization of Forest Resources, College of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanjing Forestry University; State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology; College of Chemistry and Environmental Engineering, Shenzhen University.
Image: Properties of V-NFC-CS separator and electrochemical performance of Zn||Zn cells. CC BY-NC-ND 4.0