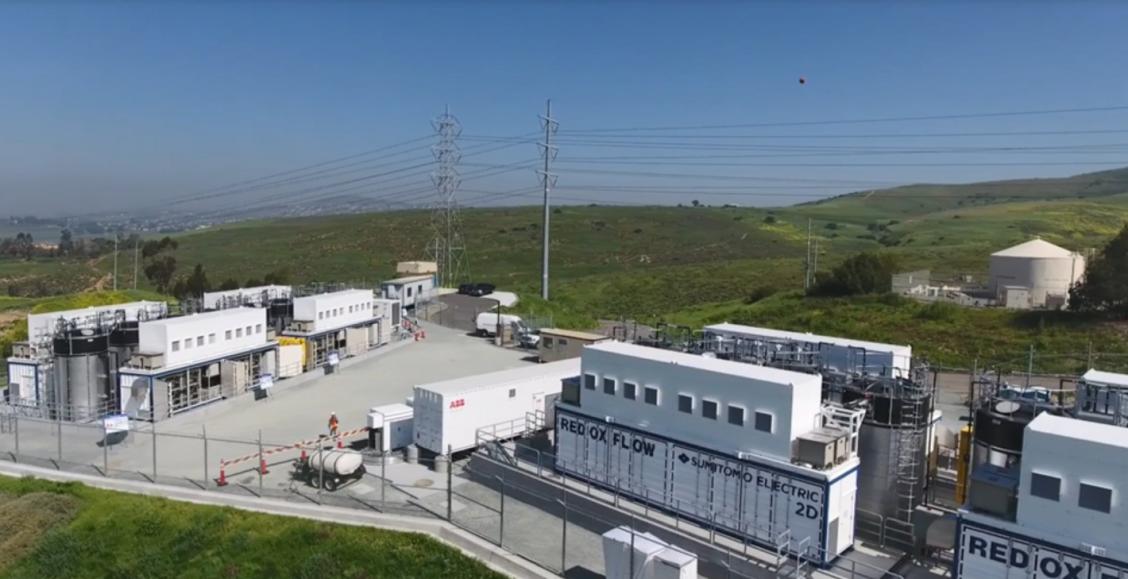
A demonstration project in the US has shown how a 2MW/8MWh redox flow battery (VRFB) can aid a “commercial” power distribution network as part of a micro-grid.
Japanese firms New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organisation (NEDO), and Sumitomo Electric Industries partnered with US utility Diego Gas & Electric (SDG&E) on the demonstration project in California to improve the power quality of the grid.
It was the first time in the US that a micro-grid has been operated on a commercial distribution network with VRFB as the main power source.
The system makes it possible to earn revenue through electricity market transactions during normal operations and provide power to blackout areas or the areas that outages are assumed, as an independent power source during an emergency such as natural disasters and planned outages.
The project began in 2015 with the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding between NEDO and the California governor’s Office of Business and Economic Development.
The flow battery was installed at SDG&E’s substation in Bonita, San Diego in 2017 as part of a collaboration between the utility and Sumitomo with project funding provided by NEDO.
Flow battery benefits
The project showed it is possible to shift from a grid-connected state to a micro-grid in either a black-start transition or a transition in which the consumers don’t notice a power outage.The results of the VRFB’s performance through the demonstration project included:
- Neither of the charge/discharge pattern, the number of cycles, nor the operational range of SOC (state of charge) accelerated battery degradation
- the decrease in the battery’s energy capacity in about four years’ time was very small (expected capacity even after 20 years, based on the demonstration results, indicates it is expected to keep the rated energy capacity (8MWh).
- Verified the high reliability of the system— no major system failures during the four years and the high availability rate (99%) of the system.
Large scale VRFB deployment
The results could inform other projects, such as micro-grids, with solar and wind power facilities constructed for off-grid areas and islands where the transportation cost of power generator fuels is expensive.
Already Sumitomo Electric has announced the start of the largest VRFB energy storage systems in the northern Japanese island of Hokkaido from April 1, news outlet Saur Energy International reported.
Sumitomo Electric said the 17MW/51MWh VRFB system will integrate local wind energy onto the grid.